Linux進程間通信之信號量
Linux進程間通信包括管道、消息隊列、System V等等,其中System V包括三種:信號量、消息隊列、共享內存,這裡只簡單介紹信號量機制。
在Linux編程中,要運用信號量實現互斥操作,用戶空間需要調用幾個系統調用,如下是一個用戶空間例子。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/sem.h>
www.2cto.com
#define SEMKEY 1234L
#define PERMS 0666
struct sembuf op_down[1]={0,-1,0};
struct sembuf op_up[1]={0,1,0};
int semid=-1;
int res;
void init_sem()
{
semid=semget(SEMKEY,0,IPC_CREAT |PERMS);
if(semid<0)
{
printf("create semaphore\n");
semid=semget(SEMKEY,1,IPC_CREAT| PERMS);
if(semid<0)
{
printf("couldn't create semaphore\n");
exit(-1);
}
res=semctl(semid,0,SETVAL,1);
}
}
void down()
{
res=semop(semid,&op_down[0],1);
}
void up()
{
res=semop(semid,&op_up[0],1);
}
int main()
{
init_sem();
printf("beforecritical code\n");
down();
printf("incritical code\n");
sleep(10);
up(); www.2cto.com
return0;
}
用戶空間的程序中分為三步:
1, 調用semget系統調用創建信號量;
2, 調用semctl系統調用設置信號量初始值;
3, 調用semop系統調用實現同步互斥控制;
下面我們一步步看看內核中都是怎麼實現的,內核中涉及到的關鍵數據結構與其主要的關系極其基本的操作如下圖所示:
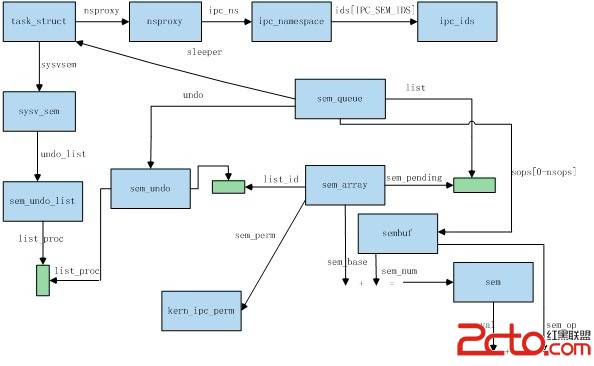
基本思路為:
一、從進程的相關命名空間中可以定位到信號量子空間,信號量ID值由IDR機制實現,semget從該IDR中獲取信號量ID。
二、信號量的核心數據結構為sem_array,所有的與同一個sem_array相關聯的sem_undo結構組成一個鏈表,所有的與同一個sem_array相關聯的待決定信號列表sem_queue組成另一個鏈表,sem_queue的項目列表在更新semval為負數值時加入(semop系統調用P操作),其部分參數為從用戶空間傳入,sem結構的定位由sem_array結構和用戶空間傳入的參數確定,當更新semval為正數時(semop系統調用V操作),喚醒對應睡眠的進程。
1,semget系統調用
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(semget,key_t, key, int, nsems, int, semflg)
{
structipc_namespace *ns;
structipc_ops sem_ops;
structipc_params sem_params;
ns = current->nsproxy->ipc_ns;
if(nsems < 0 || nsems > ns->sc_semmsl)
return-EINVAL;
sem_ops.getnew = newary;
sem_ops.associate = sem_security;
sem_ops.more_checks = sem_more_checks;
sem_params.key = key;
sem_params.flg = semflg;
sem_params.u.nsems = nsems;
returnipcget(ns, &sem_ids(ns), &sem_ops, &sem_params);
}
semget的目的是得到信號量id號。Ipcget函數會調用idr系列函數從idr中得到id號,關於idr的介紹前面兩篇文章(轉載的)寫的很詳細,就不用在說了;
2,semctl系統調用
SYSCALL_DEFINE(semctl)(int semid, intsemnum, int cmd, unionsemun arg)
{
int err = -EINVAL;
intversion;
struct ipc_namespace *ns;
if(semid < 0)
return-EINVAL;
version = ipc_parse_version(&cmd);
ns = current->nsproxy->ipc_ns;
switch(cmd){
caseIPC_INFO:
caseSEM_INFO:
caseIPC_STAT:
caseSEM_STAT:
err = semctl_nolock(ns,semid, cmd, version, arg);
returnerr;
caseGETALL: www.2cto.com
caseGETVAL:
caseGETPID:
caseGETNCNT:
caseGETZCNT:
case SETVAL:
caseSETALL:
err =semctl_main(ns,semid,semnum,cmd,version,arg);
returnerr;
caseIPC_RMID:
caseIPC_SET:
err = semctl_down(ns, semid,cmd, version, arg);
returnerr;
default:
return-EINVAL;
}
}
SETVAL是我們程序的調用路徑。
static int semctl_main(struct ipc_namespace *ns, intsemid, int semnum,
intcmd, int version, unionsemun arg)
{
structsem_array *sma;
structsem* curr;
interr;
ushort fast_sem_io[SEMMSL_FAST];
ushort* sem_io = fast_sem_io;
intnsems;
sma = sem_lock_check(ns, semid);
if(IS_ERR(sma))
returnPTR_ERR(sma);
nsems = sma->sem_nsems; www.2cto.com
err = -EACCES;
if(ipcperms (&sma->sem_perm, (cmd==SETVAL||cmd==SETALL)?S_IWUGO:S_IRUGO))
gotoout_unlock;
err = security_sem_semctl(sma, cmd);
if(err)
gotoout_unlock;
err = -EACCES;
……
err = -EINVAL;
if(semnum< 0 || semnum >= nsems)
gotoout_unlock;
curr = &sma->sem_base[semnum];
switch(cmd) {
caseGETVAL:
err = curr->semval;
gotoout_unlock;
……
caseSETVAL:
{
intval = arg.val;
structsem_undo *un;
err = -ERANGE;
if(val > SEMVMX || val < 0)
goto out_unlock;
assert_spin_locked(&sma->sem_perm.lock);
list_for_each_entry(un,&sma->list_id, list_id)
un->semadj[semnum]= 0;
curr->semval = val;
curr->sempid= task_tgid_vnr(current);
sma->sem_ctime =get_seconds();
/*maybe some queued-up processes were waiting for this */
update_queue(sma);
err = 0; www.2cto.com
gotoout_unlock;
}
}
out_unlock:
sem_unlock(sma);
out_free:
if(sem_io!= fast_sem_io)
ipc_free(sem_io, sizeof(ushort)*nsems);
returnerr;
}
設置VAL很簡單,首先從傳入的參數中獲得val的值,然後設置sem_array結構list_id鏈表中每個sem_undo結構對應信號量的調整值為0,最後設置信號量的值後調用update_queue(sma)處理對應信號量的待決操作列表,在我們這裡的執行流程中sem_queue中還沒有可用項,該待決操作列表在semtimedop系統調用啟用進程等待時添加具體的項。
/* Gothrough the pending queue for the indicated semaphore
* looking for tasks that can be completed.
*/
static voidupdate_queue (struct sem_array * sma)
{
interror;
structsem_queue * q;
q =list_entry(sma->sem_pending.next, structsem_queue, list);
while (&q->list!= &sma->sem_pending) {
error = try_atomic_semop(sma,q->sops, q->nsops,
q->undo, q->pid);
/*Does q->sleeper still need to sleep? */
if(error <= 0) {
struct sem_queue *n;
/*
* Continue scanning. The next operation
* that must be checked depends on the type ofthe
* completed operation:
* - if the operation modified the array, then
* restart from the head of the queue and
* check for threads that might be waiting
* forsemaphore values to become 0.
* - if the operation didn't modify the array,
* thenjust continue.
* The order of list_del() and reading->next
* is crucial: In the former case, thelist_del()
* must be done first [because we might be the
* first entry in ->sem_pending], in thelatter
* case the list_del() must be done last
* [because the list is invalid after thelist_del()]
*/
if (q->alter) {
list_del(&q->list);
n =list_entry(sma->sem_pending.next,
struct sem_queue, list);
} else {
n =list_entry(q->list.next, struct sem_queue,
list);
list_del(&q->list);
} www.2cto.com
/* wake up the waiting thread */
q->status =IN_WAKEUP;
wake_up_process(q->sleeper);
/* hands-off: q will disappear immediately after
* writing q->status.
*/
smp_wmb();
q->status =error;
q = n;
} else{
q =list_entry(q->list.next, struct sem_queue,list);
}
}
}
遍歷sem_array對應sem_queue鏈表中的所有項,對鏈表中的每一項sem進行操作,具體值的更改操作由函數try_atomic_semop完成,當try_atomic_semop返回非正值時,表示不需要再等待,此時喚醒等待進程。
/*
* Determine whether a sequence of semaphoreoperations would succeed
* all at once. Return 0 if yes, 1 if need tosleep, else return error code.
*/
static inttry_atomic_semop (struct sem_array * sma, struct sembuf * sops,
int nsops,struct sem_undo *un, intpid)
{
intresult, sem_op;
structsembuf *sop;
structsem * curr;
for(sop = sops; sop < sops + nsops; sop++) {
curr = sma->sem_base +sop->sem_num;
sem_op = sop->sem_op;
result = curr->semval;
if(!sem_op && result)
goto would_block;
www.2cto.com
result += sem_op;
if(result < 0)
goto would_block;
if(result > SEMVMX)
goto out_of_range;
if(sop->sem_flg & SEM_UNDO) {
int undo = un->semadj[sop->sem_num] - sem_op;
/*
* Exceedingthe undo range is an error.
*/
if (undo < (-SEMAEM - 1) || undo > SEMAEM)
goto out_of_range;
}
curr->semval = result;
}
sop--;
while(sop >= sops) {
sma->sem_base[sop->sem_num].sempid= pid;
if(sop->sem_flg & SEM_UNDO)
un->semadj[sop->sem_num]-= sop->sem_op;
sop--;
}
sma->sem_otime = get_seconds();
return0;
out_of_range:
result = -ERANGE;
gotoundo;
would_block:
if(sop->sem_flg & IPC_NOWAIT)
result = -EAGAIN;
else
result = 1;
undo:
sop--;
while(sop >= sops) {
sma->sem_base[sop->sem_num].semval-= sop->sem_op;
sop--;
}
returnresult;
}
由curr =sma->sem_base + sop->sem_num;定位到具體的sem項,然後result = curr->semval;result += sem_op;兩條語句用於對semval值進行操作。
3, semop系統調用
最終都調用semtimedop系統調用實現,
SYSCALL_DEFINE4(semtimedop,int, semid, structsembuf __user *, tsops,
unsigned,nsops, const structtimespec __user *, timeout)
{ www.2cto.com
interror = -EINVAL;
structsem_array *sma;
structsembuf fast_sops[SEMOPM_FAST];
structsembuf* sops = fast_sops, *sop;
structsem_undo *un;
intundos = 0, alter = 0, max;
structsem_queue queue;
unsignedlong jiffies_left = 0;
structipc_namespace *ns;
ns = current->nsproxy->ipc_ns;
if(nsops < 1 || semid < 0)
return-EINVAL;
if(nsops > ns->sc_semopm)
return-E2BIG;
if(nsops> SEMOPM_FAST) {
sops = kmalloc(sizeof(*sops)*nsops,GFP_KERNEL);
if(sops==NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
}
if(copy_from_user (sops, tsops, nsops * sizeof(*tsops))){
error=-EFAULT;
gotoout_free;
}
if(timeout) {
structtimespec _timeout;
if(copy_from_user(&_timeout, timeout, sizeof(*timeout))){
error = -EFAULT;
goto out_free;
}
if(_timeout.tv_sec < 0 || _timeout.tv_nsec < 0 ||
_timeout.tv_nsec>= 1000000000L){
error = -EINVAL;
goto out_free;
}
jiffies_left =timespec_to_jiffies(&_timeout);
}
max = 0;
for(sop = sops; sop < sops + nsops; sop++) {
if(sop->sem_num >= max)
max =sop->sem_num;
if(sop->sem_flg & SEM_UNDO)
undos = 1;
if(sop->sem_op != 0)
alter = 1;
}
if(undos) {
un = find_alloc_undo(ns,semid);
if(IS_ERR(un)) {
error = PTR_ERR(un);
goto out_free;
}
} else
un = NULL;
sma = sem_lock_check(ns, semid);
if(IS_ERR(sma)) {
if(un)
rcu_read_unlock();
error = PTR_ERR(sma);
gotoout_free;
}
/*
* semid identifiers are not unique - find_alloc_undomay have
* allocated an undo structure, it wasinvalidated by an RMID
* and now a new array with received the sameid. Check and fail.
* This case can be detected checkingun->semid. The existance of
* "un" itself is guaranteed by rcu.
*/
error = -EIDRM;
if (un){ www.2cto.com
if(un->semid == -1) {
rcu_read_unlock();
goto out_unlock_free;
} else{
/*
* rcu lock can be released, "un"cannot disappear:
* - sem_lock is acquired, thus IPC_RMID is
* impossible.
* - exit_sem is impossible, it always operateson
* current (or a dead task).
*/
rcu_read_unlock();
}
}
error = -EFBIG;
if (max>= sma->sem_nsems)
gotoout_unlock_free;
error = -EACCES;
if(ipcperms(&sma->sem_perm, alter ? S_IWUGO : S_IRUGO))
gotoout_unlock_free;
error = security_sem_semop(sma, sops,nsops, alter);
if(error)
gotoout_unlock_free;
error = try_atomic_semop (sma, sops,nsops, un, task_tgid_vnr(current));
if(error <= 0) {
if(alter && error == 0)
update_queue (sma);
gotoout_unlock_free;
}
/* We need tosleep on this operation, so we put the current
* task into the pending queue and go to sleep.
*/
queue.sops = sops;
queue.nsops = nsops;
queue.undo = un;
queue.pid = task_tgid_vnr(current);
queue.alter = alter;
if(alter)
list_add_tail(&queue.list,&sma->sem_pending);
else
list_add(&queue.list,&sma->sem_pending);
queue.status = -EINTR;
queue.sleeper = current;
current->state = TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE;
sem_unlock(sma);
if(timeout)
jiffies_left =schedule_timeout(jiffies_left);
else
schedule();
error = queue.status;
while(unlikely(error== IN_WAKEUP)) {
cpu_relax();
error = queue.status;
}
if(error != -EINTR) {
/*fast path: update_queue already obtained all requested
* resources */
gotoout_free;
}
sma = sem_lock(ns, semid);
if(IS_ERR(sma)) {
error = -EIDRM;
gotoout_free;
}
/*
* If queue.status != -EINTR we are woken up byanother process
*/
error = queue.status;
if(error != -EINTR) {
gotoout_unlock_free;
}
/*
* If an interrupt occurred we have to clean upthe queue
*/ www.2cto.com
if(timeout && jiffies_left == 0)
error = -EAGAIN;
list_del(&queue.list);
out_unlock_free:
sem_unlock(sma);
out_free:
if(sops!= fast_sops)
kfree(sops);
returnerror;
}
Semtimedop系統調用首先從用戶空間得到參數值,然後進行權限檢查,調用try_atomic_semop函數對sem的semval進行設置,如果需要休眠(semval值為負),將該sem_queue項初始化並添加到待決操作列表,然後重新進行調度,否則調用update_queue對隊列其他項進行操作和進程喚醒。
作者 bullbat
