日志輪轉特別適用於具有固定文件名的日志文件,比如MySQL的出錯日志、常規查詢日志、慢查詢日志 等。Linux系統有一個非常好用的根據logratate可以實現自動輪轉,本文介紹它的原理和用法。
默認情況下,logrotate部署為每天運行的cron job,你可以在目錄/etc/cron.daily裡找到名為 logrotate的配置文件。那麼它是在每天的上面時候運行的呢?打開文件/etc/crontab就知道了,下面是 我機器上的情況:
SHELL=/bin/bash
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin
MAILTO=root
HOME=/
# run-parts
01 * * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.hourly
02 4 * * * root run-parts /etc/cron.daily
22 4 * * 0 root run-parts /etc/cron.weekly
42 4 1 * * root run-parts /etc/cron.monthly
從上面的配置我們可以知道,/etc/cron.daily是在每天凌晨4:02執行。也就是說,每天4:02 分/etc/cron.daily/logrotate將會自動執行,下面是它的內容:
#!/bin/sh
/usr/sbin/logrotate /etc/logrotate.conf
EXITVALUE=$?
if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]"
fi
exit 0
從上面我們可以知道,logratate默認的配置文件是/etc/logratate.conf,下面是它的內容:
EXITVALUE=$?
if [ $EXITVALUE != 0 ]; then
/usr/bin/logger -t logrotate "ALERT exited abnormally with [$EXITVALUE]"
fi
exit 0
[root@lx202 /etc/cron.daily ]# cat /etc/logrotate.conf
# see "man logrotate" for details
# rotate log files weekly
weekly
# keep 4 weeks worth of backlogs
rotate 4
# create new (empty) log files after rotating old ones
create
# uncomment this if you want your log files compressed
#compress
# RPM packages drop log rotation information into this directory
include /etc/logrotate.d
# no packages own wtmp -- we'll rotate them here
/var/log/wtmp {
monthly
minsize 1M
create 0664 root utmp
rotate 1
}
/var/log/btmp {
missingok
monthly
minsize 1M
create 0600 root utmp
rotate 1
}
從上面我們可以知道,這個默認的配置文件將讀取目錄/etc/logrotate.d,所以我們只要把自己寫的 配置文件放到該目錄下即可。
MySQL本省提供了一個rotate的參考配置文件,在support-files目錄下,文件名為mysql-log-rotate ,內容如下:
# This logname can be set in /etc/my.cnf
# by setting the variable "err-log"
# in the [safe_mysqld] section as follows:
#
# [safe_mysqld]
# err-log=/opt/mysql/data/mysqld.log
#
# If the root user has a password you have to create a
# /root/.my.cnf configuration file with the following
# content:
#
# [mysqladmin]
# password = <secret>
# user= root
#
# where "<secret>" is the password.
#
# ATTENTION: This /root/.my.cnf should be readable ONLY
# for root !
/opt/mysql/data/mysqld.log {
# create 600 mysql mysql
notifempty
daily
rotate 3
missingok
compress
postrotate
# just if mysqld is really running
if test -x /opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin && \
/opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin ping &>/dev/null
then
/opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin flush-logs
fi
endscript
}
logrotate常見選項:
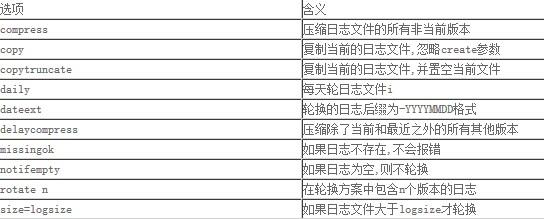
我們只要根據自己的需要,修改相應配置即可,下面是一個例子:
1)創建MySQL root密碼文件
vi /root/.my.cnf
[mysqladmin] password = *** user= root
chmod 600 /root/.my.cnf
2)把mysql-log-rotate拷貝至/etc/logrotate.d目錄下,修改其內容為 :
/data/mysql/log/slow.log
/data/mysql/log/alert.log {
create 600 mysql mysql
notifempty
daily
rotate 7
missingok
# compress
postrotate
# just if mysqld is really running
if test -x /opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin && \
/opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin ping &>/dev/null
then
/opt/mysql/bin/mysqladmin flush-logs
fi
endscript
}
3)執行以下命令測試
/usr/sbin/logrotate -f /etc/logrotate.d/mysql-log-rotate