大家好,今天我們來學習一下如何在 Docker 容器裡運行的 Nginx Web 服務器中安裝 WordPress。WordPress 是一個很好的免費開源的內容管理系統,全球成千上萬的網站都在使用它。Docker 是一個開源項目,提供了一個可以打包、裝載和運行任何應用的輕量級容器的開放平台。它沒有語言支持、框架和打包系統的限制,從小型的家用電腦到高端服務 器,在何時何地都可以運行。這使它們可以不依賴於特定軟件棧和供應商,像一塊塊積木一樣部署和擴展網絡應用、數據庫和後端服務。
今天,我們會在 docker 容器上部署最新的 WordPress 軟件包,包括需要的前提條件,例如 Nginx Web 服務器、PHP5、MariaDB 服務器等。下面是在運行在 Docker 容器上成功安裝 WordPress 的簡單步驟。
在我們真正開始之前,我們需要確保在我們的 Linux 機器上已經安裝了 Docker。我們使用的主機是 CentOS 7,因此我們用下面的命令使用 yum 管理器安裝 docker。
# yum install docker
# systemctl restart docker.service
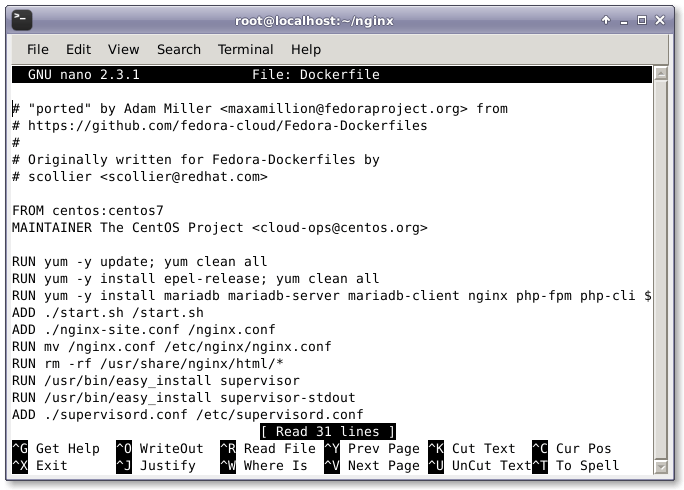
我們需要創建用於自動安裝 wordpress 以及其前置需求的 Dockerfile。這個 Dockerfile 將用於構建 WordPress 的安裝鏡像。這個 WordPress Dockerfile 會從 Docker Registry Hub 獲取 CentOS 7 鏡像並用最新的可用更新升級系統。然後它會安裝必要的軟件,例如 Nginx Web 服務器、PHP、MariaDB、Open SSH 服務器,以及其它保證 Docker 容器正常運行不可缺少的組件。最後它會執行一個初始化 WordPress 安裝的腳本。
# nano Dockerfile
然後,我們需要將下面的配置行添加到 Dockerfile中。
FROM centos:centos7 MAINTAINER The CentOS Project <[email protected]> RUN yum -y update; yum clean all RUN yum -y install epel-release; yum clean all RUN yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server mariadb-client nginx php-fpm php-cli php-mysql php-gd php-imap php-ldap php-odbc php-pear php-xml php-xmlrpc php-magickwand php-magpierss php-mbstring php-mcrypt php-mssql php-shout php-snmp php-soap php-tidy php-apc pwgen python-setuptools curl git tar; yum clean all ADD ./start.sh /start.sh ADD ./nginx-site.conf /nginx.conf RUN mv /nginx.conf /etc/nginx/nginx.conf RUN rm -rf /usr/share/nginx/html/* RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor RUN /usr/bin/easy_install supervisor-stdout ADD ./supervisord.conf /etc/supervisord.conf RUN echo %sudo ALL=NOPASSWD: ALL >> /etc/sudoers ADD http://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz /wordpress.tar.gz RUN tar xvzf /wordpress.tar.gz RUN mv /wordpress/* /usr/share/nginx/html/. RUN chown -R apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/ RUN chmod 755 /start.sh RUN mkdir /var/run/sshd EXPOSE 80 EXPOSE 22 CMD ["/bin/bash", "/start.sh"]
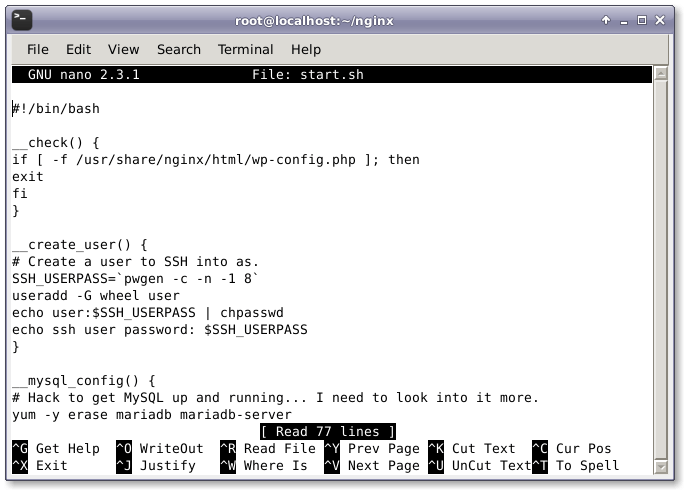
我們創建了 Dockerfile 之後,我們需要創建用於運行和配置 WordPress 安裝的腳本,名稱為 start.sh。它會為 WordPress 創建並配置數據庫和密碼。用我們喜歡的文本編輯器打開 start.sh。
# nano start.sh
打開 start.sh 之後,我們要添加下面的配置行到文件中。
#!/bin/bash
__check() {
if [ -f /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php ]; then
exit
fi
}
__create_user() {
# 創建用於 SSH 登錄的用戶
SSH_USERPASS=`pwgen -c -n -1 8`
useradd -G wheel user
echo user:$SSH_USERPASS | chpasswd
echo ssh user password: $SSH_USERPASS
}
__mysql_config() {
# 啟用並運行 MySQL
yum -y erase mariadb mariadb-server
rm -rf /var/lib/mysql/ /etc/my.cnf
yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
mysql_install_db
chown -R mysql:mysql /var/lib/mysql
/usr/bin/mysqld_safe &
sleep 10
}
__handle_passwords() {
# 在這裡我們生成隨機密碼(多虧了 pwgen)。前面兩個用於 mysql 用戶,最後一個用於 wp-config.php 的隨機密鑰。
WORDPRESS_DB="wordpress"
MYSQL_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
WORDPRESS_PASSWORD=`pwgen -c -n -1 12`
# 這是在日志中顯示的密碼。
echo mysql root password: $MYSQL_PASSWORD
echo wordpress password: $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD
echo $MYSQL_PASSWORD > /mysql-root-pw.txt
echo $WORDPRESS_PASSWORD > /wordpress-db-pw.txt
# 這裡原來是一個包括 sed、cat、pipe 和 stuff 的很長的行,但多虧了
# @djfiander 的 https://gist.github.com/djfiander/6141138
# 現在沒有了
sed -e "s/database_name_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/username_here/$WORDPRESS_DB/
s/password_here/$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD/
/'AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_KEY'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'SECURE_AUTH_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'LOGGED_IN_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/
/'NONCE_SALT'/s/put your unique phrase here/`pwgen -c -n -1 65`/" /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config-sample.php > /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__httpd_perms() {
chown apache:apache /usr/share/nginx/html/wp-config.php
}
__start_mysql() {
# systemctl 啟動 mysqld 服務
mysqladmin -u root password $MYSQL_PASSWORD
mysql -uroot -p$MYSQL_PASSWORD -e "CREATE DATABASE wordpress; GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO 'wordpress'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY '$WORDPRESS_PASSWORD'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;"
killall mysqld
sleep 10
}
__run_supervisor() {
supervisord -n
}
# 調用所有函數
__check
__create_user
__mysql_config
__handle_passwords
__httpd_perms
__start_mysql
__run_supervisor
增加完上面的配置之後,保存並關閉文件。
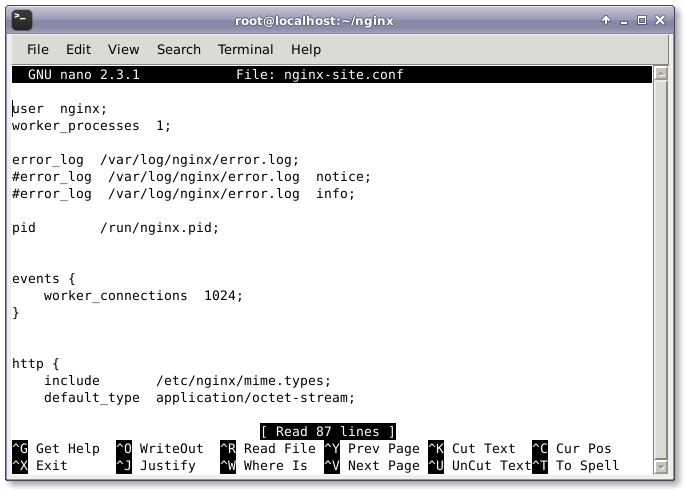
現在,我們需要創建 Nginx Web 服務器的配置文件,命名為 nginx-site.conf。
# nano nginx-site.conf
然後,增加下面的配置信息到配置文件。
user nginx;
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log notice;
#error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log info;
pid /run/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
# Load modular configuration files from the /etc/nginx/conf.d directory.
# See http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html#include
# for more information.
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
location ~ \.php$ {
root /usr/share/nginx/html;
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
}
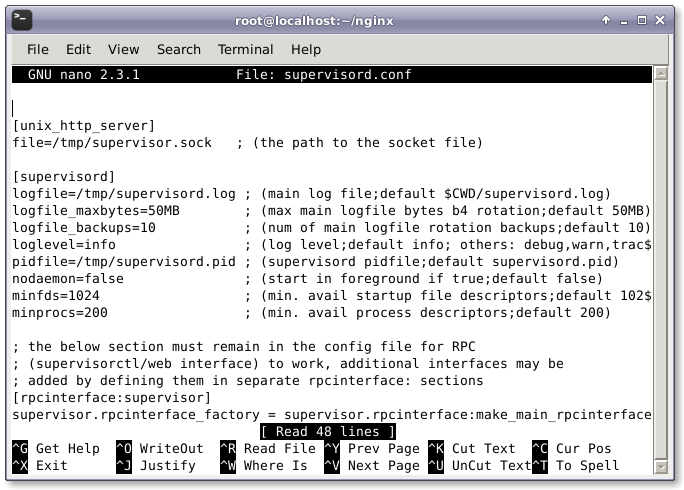
現在,創建 supervisor.conf 文件並添加下面的行。
# nano supervisord.conf
然後,添加以下行。
[unix_http_server] file=/tmp/supervisor.sock ; (the path to the socket file) [supervisord] logfile=/tmp/supervisord.log ; (main log file;default $CWD/supervisord.log) logfile_maxbytes=50MB ; (max main logfile bytes b4 rotation;default 50MB) logfile_backups=10 ; (num of main logfile rotation backups;default 10) loglevel=info ; (log level;default info; others: debug,warn,trace) pidfile=/tmp/supervisord.pid ; (supervisord pidfile;default supervisord.pid) nodaemon=false ; (start in foreground if true;default false) minfds=1024 ; (min. avail startup file descriptors;default 1024) minprocs=200 ; (min. avail process descriptors;default 200) ; the below section must remain in the config file for RPC ; (supervisorctl/web interface) to work, additional interfaces may be ; added by defining them in separate rpcinterface: sections [rpcinterface:supervisor] supervisor.rpcinterface_factory = supervisor.rpcinterface:make_main_rpcinterface [supervisorctl] serverurl=unix:///tmp/supervisor.sock ; use a unix:// URL for a unix socket [program:php-fpm] command=/usr/sbin/php-fpm -c /etc/php/fpm stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:php-fpm-log] command=tail -f /var/log/php-fpm/php-fpm.log stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:mysql] command=/usr/bin/mysql --basedir=/usr --datadir=/var/lib/mysql --plugin-dir=/usr/lib/mysql/plugin --user=mysql --log-error=/var/log/mysql/error.log --pid-file=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.pid --socket=/var/run/mysqld/mysqld.sock --port=3306 stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [program:nginx] command=/usr/sbin/nginx stdout_events_enabled=true stderr_events_enabled=true [eventlistener:stdout] command = supervisor_stdout buffer_size = 100 events = PROCESS_LOG result_handler = supervisor_stdout:event_handler
添加完後,保存並關閉文件。
現在,完成了創建配置文件和腳本之後,我們終於要使用 Dockerfile 來創建安裝最新的 WordPress CMS(譯者注:Content Management System,內容管理系統)所需要的容器,並根據配置文件進行配置。做到這點,我們需要在對應的目錄中運行以下命令。
# docker build --rm -t wordpress:centos7 .
現在,執行以下命令運行新構建的容器,並為 Nginx Web 服務器和 SSH 訪問打開88 和 22號相應端口 。
# CID=$(docker run -d -p 80:80 wordpress:centos7)

運行以下命令檢查進程以及容器內部執行的命令。
# echo "$(docker logs $CID )"
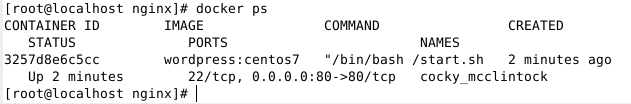
運行以下命令檢查端口映射是否正確。
# docker ps
最後如果一切正常的話,當我們用浏覽器打開 http://ip-address/ 或者 http://mywebsite.com/ 的時候會看到 WordPress 的歡迎界面。
現在,我們將通過 Web 界面為 WordPress 面板設置 WordPress 的配置、用戶名和密碼。
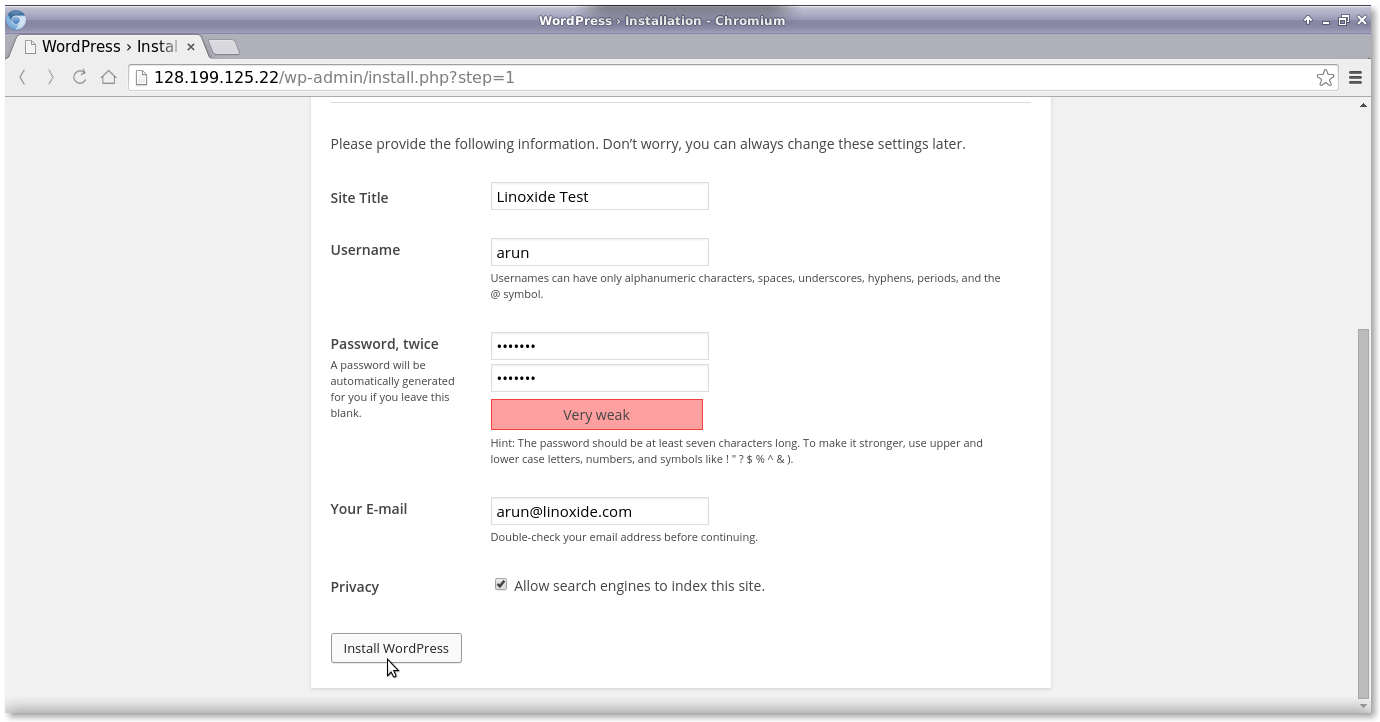
然後,用上面用戶名和密碼輸入到 WordPress 登錄界面。